There is only one function for creating a new TextView widget.
textview = gtk.TextView(buffer=None) |
When a TextView is created it will create an associated TextBuffer and TextTagTable by default. If you want to use an existing TextBuffer in a TextView specify it in the above method. To change the TextBuffer used by a TextView use the following method:
textview.set_buffer(buffer) |
Use the following method to retrieve a reference to the TextBuffer from a TextView:
buffer = textview.get_buffer() |
A TextView widget doesn't have scrollbars to adjust the view in case the text is larger than the window. To provide scrollbars, you add the TextView to a ScrolledWindow (see Section 10.9, “Scrolled Windows”).
A TextView can be used to allow the user to edit a body of text, or to display multiple lines of read-only text to the user. To switch between these modes of operation, the use the following method:
textview.set_editable(setting) |
The setting argument is a TRUE or FALSE value that specifies whether the user is permitted to edit the contents of the TextView widget. The editable mode of the TextView can be overridden in text ranges within the TextBuffer by TextTags.
You can retrieve the current editable setting using the method:
setting = textview.get_editable() |
When the TextView is not editable, you probably should hide the cursor using the method:
textview.set_cursor_visible(setting) |
The setting argument is a TRUE or FALSE value that specifies whether the cursor should be visible The TextView can wrap lines of text that are too long to fit onto a single line of the display window. Its default behavior is to not wrap lines. This can be changed using the next method:
textview.set_wrap_mode(wrap_mode) |
This method allows you to specify that the text widget should wrap long lines on word or character boundaries. The word_wrap argument is one of:
gtk.WRAP_NONE gtk.WRAP_CHAR gtk.WRAP_WORD |
The default justification of the text in a TextView can be set and retrieved using the methods:
textview.set_justification(justification) justification = textview.get_justification() |
where justification is one of:
gtk.JUSTIFY_LEFT gtk.JUSTIFY_RIGHT gtk.JUSTIFY_CENTER |
Note
The justification will be JUSTIFY_LEFT if the wrap_mode is WRAP_NONE. Tags in the associated TextBuffer may override the default justification.
Other default attributes that can be set and retrieved in a TextView are: left margin, right margin, tabs, and paragraph indentation using the following methods:
textview.set_left_margin(left_margin) left_margin = textview.get_left_margin() textview.set_right_margin(right_margin) right_margin = textview.get_right_margin() textview.set_indent(indent) indent = textview.get_indent() textview.set_pixels_above_lines(pixels_above_line) pixels_above_line = textview.get_pixels_above_lines() textview.set_pixels_below_lines(pixels_below_line) pixels_below_line = textview.get_pixels_below_lines() textview.set_pixels_inside_wrap(pixels_inside_wrap) pixels_inside_wrap = textview.get_pixels_inside_wrap() textview.set_tabs(tabs) tabs = textview.get_tabs() |
left_margin, right_margin, indent, pixels_above_lines, pixels_below_lines and pixels_inside_wrap are specified in pixels. These default values may be overridden by tags in the associated TextBuffer. tabs is a pango.TabArray.
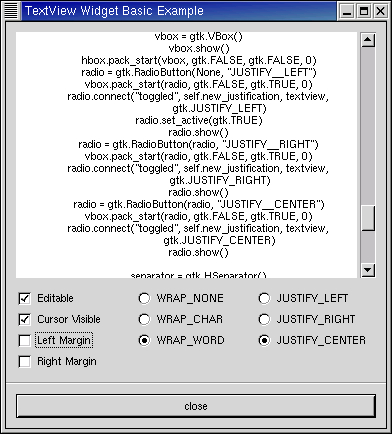
The textview-basic.py example program illustrates basic use of the TextView widget:
The source code for the program is:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2
3 # example textview-basic.py
4
5 import pygtk
6 pygtk.require('2.0')
7 import gtk
8
9 class TextViewExample:
10 def toggle_editable(self, checkbutton, textview):
11 textview.set_editable(checkbutton.get_active())
12
13 def toggle_cursor_visible(self, checkbutton, textview):
14 textview.set_cursor_visible(checkbutton.get_active())
15
16 def toggle_left_margin(self, checkbutton, textview):
17 if checkbutton.get_active():
18 textview.set_left_margin(50)
19 else:
20 textview.set_left_margin(0)
21
22 def toggle_right_margin(self, checkbutton, textview):
23 if checkbutton.get_active():
24 textview.set_right_margin(50)
25 else:
26 textview.set_right_margin(0)
27
28 def new_wrap_mode(self, radiobutton, textview, val):
29 if radiobutton.get_active():
30 textview.set_wrap_mode(val)
31
32 def new_justification(self, radiobutton, textview, val):
33 if radiobutton.get_active():
34 textview.set_justification(val)
35
36 def close_application(self, widget):
37 gtk.main_quit()
38
39 def __init__(self):
40 window = gtk.Window(gtk.WINDOW_TOPLEVEL)
41 window.set_resizable(True)
42 window.connect("destroy", self.close_application)
43 window.set_title("TextView Widget Basic Example")
44 window.set_border_width(0)
45
46 box1 = gtk.VBox(False, 0)
47 window.add(box1)
48 box1.show()
49
50 box2 = gtk.VBox(False, 10)
51 box2.set_border_width(10)
52 box1.pack_start(box2, True, True, 0)
53 box2.show()
54
55 sw = gtk.ScrolledWindow()
56 sw.set_policy(gtk.POLICY_AUTOMATIC, gtk.POLICY_AUTOMATIC)
57 textview = gtk.TextView()
58 textbuffer = textview.get_buffer()
59 sw.add(textview)
60 sw.show()
61 textview.show()
62
63 box2.pack_start(sw)
64 # Load the file textview-basic.py into the text window
65 infile = open("textview-basic.py", "r")
66
67 if infile:
68 string = infile.read()
69 infile.close()
70 textbuffer.set_text(string)
71
72 hbox = gtk.HButtonBox()
73 box2.pack_start(hbox, False, False, 0)
74 hbox.show()
75
76 vbox = gtk.VBox()
77 vbox.show()
78 hbox.pack_start(vbox, False, False, 0)
79 # check button to toggle editable mode
80 check = gtk.CheckButton("Editable")
81 vbox.pack_start(check, False, False, 0)
82 check.connect("toggled", self.toggle_editable, textview)
83 check.set_active(True)
84 check.show()
85 # check button to toggle cursor visiblity
86 check = gtk.CheckButton("Cursor Visible")
87 vbox.pack_start(check, False, False, 0)
88 check.connect("toggled", self.toggle_cursor_visible, textview)
89 check.set_active(True)
90 check.show()
91 # check button to toggle left margin
92 check = gtk.CheckButton("Left Margin")
93 vbox.pack_start(check, False, False, 0)
94 check.connect("toggled", self.toggle_left_margin, textview)
95 check.set_active(False)
96 check.show()
97 # check button to toggle right margin
98 check = gtk.CheckButton("Right Margin")
99 vbox.pack_start(check, False, False, 0)
100 check.connect("toggled", self.toggle_right_margin, textview)
101 check.set_active(False)
102 check.show()
103 # radio buttons to specify wrap mode
104 vbox = gtk.VBox()
105 vbox.show()
106 hbox.pack_start(vbox, False, False, 0)
107 radio = gtk.RadioButton(None, "WRAP__NONE")
108 vbox.pack_start(radio, False, True, 0)
109 radio.connect("toggled", self.new_wrap_mode, textview, gtk.WRAP_NONE)
110 radio.set_active(True)
111 radio.show()
112 radio = gtk.RadioButton(radio, "WRAP__CHAR")
113 vbox.pack_start(radio, False, True, 0)
114 radio.connect("toggled", self.new_wrap_mode, textview, gtk.WRAP_CHAR)
115 radio.show()
116 radio = gtk.RadioButton(radio, "WRAP__WORD")
117 vbox.pack_start(radio, False, True, 0)
118 radio.connect("toggled", self.new_wrap_mode, textview, gtk.WRAP_WORD)
119 radio.show()
120
121 # radio buttons to specify justification
122 vbox = gtk.VBox()
123 vbox.show()
124 hbox.pack_start(vbox, False, False, 0)
125 radio = gtk.RadioButton(None, "JUSTIFY__LEFT")
126 vbox.pack_start(radio, False, True, 0)
127 radio.connect("toggled", self.new_justification, textview,
128 gtk.JUSTIFY_LEFT)
129 radio.set_active(True)
130 radio.show()
131 radio = gtk.RadioButton(radio, "JUSTIFY__RIGHT")
132 vbox.pack_start(radio, False, True, 0)
133 radio.connect("toggled", self.new_justification, textview,
134 gtk.JUSTIFY_RIGHT)
135 radio.show()
136 radio = gtk.RadioButton(radio, "JUSTIFY__CENTER")
137 vbox.pack_start(radio, False, True, 0)
138 radio.connect("toggled", self.new_justification, textview,
139 gtk.JUSTIFY_CENTER)
140 radio.show()
141
142 separator = gtk.HSeparator()
143 box1.pack_start(separator, False, True, 0)
144 separator.show()
145
146 box2 = gtk.VBox(False, 10)
147 box2.set_border_width(10)
148 box1.pack_start(box2, False, True, 0)
149 box2.show()
150
151 button = gtk.Button("close")
152 button.connect("clicked", self.close_application)
153 box2.pack_start(button, True, True, 0)
154 button.set_flags(gtk.CAN_DEFAULT)
155 button.grab_default()
156 button.show()
157 window.show()
158
159 def main():
160 gtk.main()
161 return 0
162
163 if __name__ == "__main__":
164 TextViewExample()
165 main()
|
Lines 10-34 define the callbacks for the radio and check buttons used to change the default attributes of the TextView. Lines 55-63 create a ScrolledWindow to contain the TextView. The ScrolledWindow is packed into a VBox with the check and radio buttons created in lines 72-140. The TextBuffer associated with the TextView is loaded with the contents of the source file in lines 64-70.