The method drag_source_set() specifies a set of target types for a drag operation on a widget.
widget.drag_source_set(start_button_mask, targets, actions) |
The parameters signify the following:
widget specifies the drag source widget
start_button_mask specifies a bitmask of buttons that can start the drag (e.g. BUTTON1_MASK)
targets specifies a list of target data types the drag will support
actions specifies a bitmask of possible actions for a drag from this window
The targets parameter is a list of tuples each similar to:
(target, flags, info) |
target specifies a string representing the drag type.
flags restrict the drag scope. flags can be set to 0 (no limitation of scope) or the following flags:
gtk.TARGET_SAME_APP # Target will only be selected for drags within a single application. gtk.TARGET_SAME_WIDGET # Target will only be selected for drags within a single widget. |
info is an application assigned integer identifier.
If a widget is no longer required to act as a source for drag-and-drop operations, the method drag_source_unset() can be used to remove a set of drag-and-drop target types.
widget.drag_source_unset() |
The source widget is sent the following signals during a drag-and-drop operation.
Table 22.1. Source Widget Signals
| drag_begin | def drag_begin_cb(widget, drag_context, data): |
| drag_data_get | def drag_data_get_cb(widget, drag_context, selection_data, info, time, data): |
| drag_data_delete | def drag_data_delete_cb(widget, drag_context, data): |
| drag_end | def drag_end_cb(widget, drag_context, data): |
The "drag-begin" signal handler can be used to set up some inital conditions such as a drag icon using one of the Widget methods: drag_source_set_icon(), drag_source_set_icon_pixbuf(), drag_source_set_icon_stock(). The "drag-end' signal handler can be used to undo the actions of the "drag-begin" signal ahndler.
The "drag-data-get" signal handler should return the drag data matching the target specified by info. It fills in the gtk.gdk.SelectionData with the drag data.
The "drag-delete" signal handler is used to delete the drag data for a gtk.gdk.ACTION_MOVE action after the data has been copied.
The drag_dest_set() method specifies that this widget can receive drops and specifies what types of drops it can receive.
drag_dest_unset() specifies that the widget can no longer receive drops.
widget.drag_dest_set(flags, targets, actions) widget.drag_dest_unset() |
flags specifies what actions GTK+ should take on behalf of widget for drops on it. The possible values of flags are:
| gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_MOTION | If set for a widget, GTK+, during a drag over this widget will check if the drag matches this widget's list of possible targets and actions. GTK+ will then call drag_status() as appropriate. |
| gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_HIGHLIGHT | If set for a widget, GTK+ will draw a highlight on this widget as long as a drag is over this widget and the widget drag format and action is acceptable. |
| gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_DROP | If set for a widget, when a drop occurs, GTK+ will check if the drag matches this widget's list of possible targets and actions. If so, GTK+ will call drag_get_data() on behalf of the widget. Whether or not the drop is succesful, GTK+ will call drag_finish(). If the action was a move and the drag was succesful, then TRUE will be passed for the delete parameter to drag_finish(). |
| gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_ALL | If set, specifies that all default actions should be taken. |
targets is a list of target information tuples as described above.
actions is a bitmask of possible actions for a drag onto this widget. The possible values that can be or'd for actions are:
gtk.gdk.ACTION_DEFAULT gtk.gdk.ACTION_COPY gtk.gdk.ACTION_MOVE gtk.gdk.ACTION_LINK gtk.gdk.ACTION_PRIVATE gtk.gdk.ACTION_ASK |
targets and actions are ignored if flags does not contain gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_MOTION or gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_DROP. In that case the application must handle the "drag-motion" and "drag-drop" signals.
The "drag-motion" handler must determine if the drag data is appropriate by matching the destination targets with the gtk.gdk.DragContext targets and optionally by examining the drag data by calling the drag_get_data() method. The gtk.gdk.DragContext. drag_status() method must be called to update the drag_context status.
The "drag-drop" handler must determine the matching target using the Widget drag_dest_find_target() method and then ask for the drag data using the Widget drag_get_data() method. The data will be available in the "drag-data-received" handler.
The dragtargets.py program prints out the targets of a drag operation in a label:
1 #!/usr/local/env python
2
3 import pygtk
4 pygtk.require('2.0')
5 import gtk
6
7 def motion_cb(wid, context, x, y, time):
8 context.drag_status(gtk.gdk.ACTION_COPY, time)
9 return True
10
11 def drop_cb(wid, context, x, y, time):
12 l.set_text('\n'.join([str(t) for t in context.targets]))
13 return True
14
15 w = gtk.Window()
16 w.set_size_request(200, 150)
17 w.drag_dest_set(0, [], 0)
18 w.connect('drag_motion', motion_cb)
19 w.connect('drag_drop', drop_cb)
20 w.connect('destroy', lambda w: gtk.main_quit())
21 l = gtk.Label()
22 w.add(l)
23 w.show_all()
24
25 gtk.main()
|
The program creates a window and then sets it as a drag destination for no targets and actions by setting the flags to zero. The motion_cb() and drop_cb() handlers are connected to the "drag-motion" and "drag-drop" signals respectively. The motion_cb() handler just sets the drag status for the drag context so that a drop will be enabled. The drop_cb() sets the label text to a string containing the drag targets and ignores the data so the drop never completes.
The destination widget is sent the following signals during a drag-and-drop operation.
Table 22.2. Destination Widget Signals
| drag_motion | def drag_motion_cb(widget, drag_context, x, y, time, data): |
| drag_drop | def drag_drop_cb(widget, drag_context, x, y, time, data): |
| drag_data_received | def drag_data_received_cb(widget, drag_context, x, y, selection_data, info, time, data): |
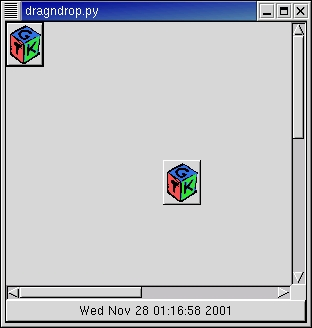
The dragndrop.py example program demonstrates the use of drag and drop in one application. A button with a xpm pixmap (in gtkxpm.py) is the source for the drag; it provides both text and xpm data. A layout widget is the destination for the xpm drop while a button is the destination for the text drop. Figure 22.1, “Drag and Drop Example” illustrates the program display after an xpm drop has been made on the layout and a text drop has been made on the button:
The dragndrop.py source code is:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2
3 # example dragndrop.py
4
5 import pygtk
6 pygtk.require('2.0')
7 import gtk
8 import string, time
9
10 import gtkxpm
11
12 class DragNDropExample:
13 HEIGHT = 600
14 WIDTH = 600
15 TARGET_TYPE_TEXT = 80
16 TARGET_TYPE_PIXMAP = 81
17 fromImage = [ ( "text/plain", 0, TARGET_TYPE_TEXT ),
18 ( "image/x-xpixmap", 0, TARGET_TYPE_PIXMAP ) ]
19 toButton = [ ( "text/plain", 0, TARGET_TYPE_TEXT ) ]
20 toCanvas = [ ( "image/x-xpixmap", 0, TARGET_TYPE_PIXMAP ) ]
21
22 def layout_resize(self, widget, event):
23 x, y, width, height = widget.get_allocation()
24 if width > self.lwidth or height > self.lheight:
25 self.lwidth = max(width, self.lwidth)
26 self.lheight = max(height, self.lheight)
27 widget.set_size(self.lwidth, self.lheight)
28
29 def makeLayout(self):
30 self.lwidth = self.WIDTH
31 self.lheight = self.HEIGHT
32 box = gtk.VBox(False,0)
33 box.show()
34 table = gtk.Table(2, 2, False)
35 table.show()
36 box.pack_start(table, True, True, 0)
37 layout = gtk.Layout()
38 self.layout = layout
39 layout.set_size(self.lwidth, self.lheight)
40 layout.connect("size-allocate", self.layout_resize)
41 layout.show()
42 table.attach(layout, 0, 1, 0, 1, gtk.FILL|gtk.EXPAND,
43 gtk.FILL|gtk.EXPAND, 0, 0)
44 # create the scrollbars and pack into the table
45 vScrollbar = gtk.VScrollbar(None)
46 vScrollbar.show()
47 table.attach(vScrollbar, 1, 2, 0, 1, gtk.FILL|gtk.SHRINK,
48 gtk.FILL|gtk.SHRINK, 0, 0)
49 hScrollbar = gtk.HScrollbar(None)
50 hScrollbar.show()
51 table.attach(hScrollbar, 0, 1, 1, 2, gtk.FILL|gtk.SHRINK,
52 gtk.FILL|gtk.SHRINK,
53 0, 0)
54 # tell the scrollbars to use the layout widget's adjustments
55 vAdjust = layout.get_vadjustment()
56 vScrollbar.set_adjustment(vAdjust)
57 hAdjust = layout.get_hadjustment()
58 hScrollbar.set_adjustment(hAdjust)
59 layout.connect("drag_data_received", self.receiveCallback)
60 layout.drag_dest_set(gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_MOTION |
61 gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_HIGHLIGHT |
62 gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_DROP,
63 self.toCanvas, gtk.gdk.ACTION_COPY)
64 self.addImage(gtkxpm.gtk_xpm, 0, 0)
65 button = gtk.Button("Text Target")
66 button.show()
67 button.connect("drag_data_received", self.receiveCallback)
68 button.drag_dest_set(gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_MOTION |
69 gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_HIGHLIGHT |
70 gtk.DEST_DEFAULT_DROP,
71 self.toButton, gtk.gdk.ACTION_COPY)
72 box.pack_start(button, False, False, 0)
73 return box
74
75 def addImage(self, xpm, xd, yd):
76 hadj = self.layout.get_hadjustment()
77 vadj = self.layout.get_vadjustment()
78 style = self.window.get_style()
79 pixmap, mask = gtk.gdk.pixmap_create_from_xpm_d(
80 self.window.window, style.bg[gtk.STATE_NORMAL], xpm)
81 image = gtk.Image()
82 image.set_from_pixmap(pixmap, mask)
83 button = gtk.Button()
84 button.add(image)
85 button.connect("drag_data_get", self.sendCallback)
86 button.drag_source_set(gtk.gdk.BUTTON1_MASK, self.fromImage,
87 gtk.gdk.ACTION_COPY)
88 button.show_all()
89 # have to adjust for the scrolling of the layout - event location
90 # is relative to the viewable not the layout size
91 self.layout.put(button, int(xd+hadj.value), int(yd+vadj.value))
92 return
93
94 def sendCallback(self, widget, context, selection, targetType, eventTime):
95 if targetType == self.TARGET_TYPE_TEXT:
96 now = time.time()
97 str = time.ctime(now)
98 selection.set(selection.target, 8, str)
99 elif targetType == self.TARGET_TYPE_PIXMAP:
100 selection.set(selection.target, 8,
101 string.join(gtkxpm.gtk_xpm, '\n'))
102
103 def receiveCallback(self, widget, context, x, y, selection, targetType,
104 time):
105 if targetType == self.TARGET_TYPE_TEXT:
106 label = widget.get_children()[0]
107 label.set_text(selection.data)
108 elif targetType == self.TARGET_TYPE_PIXMAP:
109 self.addImage(string.split(selection.data, '\n'), x, y)
110
111 def __init__(self):
112 self.window = gtk.Window(gtk.WINDOW_TOPLEVEL)
113 self.window.set_default_size(300, 300)
114 self.window.connect("destroy", lambda w: gtk.main_quit())
115 self.window.show()
116 layout = self.makeLayout()
117 self.window.add(layout)
118
119 def main():
120 gtk.main()
121
122 if __name__ == "__main__":
123 DragNDropExample()
124 main()
|