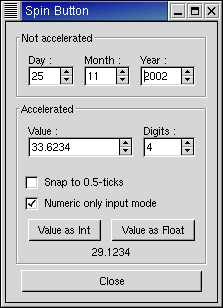
The SpinButton widget is generally used to allow the user to select a value from a range of numeric values. It consists of a text entry box with up and down arrow buttons attached to the side. Selecting one of the buttons causes the value to "spin" up and down the range of possible values. The entry box may also be edited directly to enter a specific value.
The SpinButton allows the value to have zero or more decimal places and to be incremented/decremented in configurable steps. The action of holding down one of the buttons optionally results in an acceleration of change in the value according to how long it is depressed.
The SpinButton uses an Adjustment (see Chapter 7, Adjustments) object to hold information about the range of values that the spin button can take. This makes for a powerful SpinButton widget.
Recall that an Adjustment widget is created with the following function, which illustrates the information that it holds:
adjustment = gtk.Adjustment(value=0, lower=0, upper=0, step_incr=0, page_incr=0, page_size=0) |
These attributes of an Adjustment are used by the SpinButton in the following way:
| value | initial value for the Spin Button |
| lower | lower range value |
| upper | upper range value |
| step_increment | value to increment/decrement when pressing mouse on a button |
| page_increment | value to increment/decrement when pressing mouse on a button |
| page_size | unused |
Additionally, mouse can be used to jump directly to the upper or lower values when used to select one of the buttons. Lets look at how to create a SpinButton:
spin_button = gtk.SpinButton(adjustment=None, climb_rate=0.0, digits=0) |
The climb_rate argument take a value between 0.0 and 1.0 and indicates the amount of acceleration that the SpinButton has. The digits argument specifies the number of decimal places to which the value will be displayed.
A SpinButton can be reconfigured after creation using the following method:
spin_button.configure(adjustment, climb_rate, digits) |
The spin_button argument specifies the SpinButton widget that is to be reconfigured. The other arguments are as specified above.
The adjustment can be set and retrieved independently using the following two methods:
spin_button.set_adjustment(adjustment) adjustment = spin_button.get_adjustment() |
The number of decimal places can also be altered using:
spin_button.set_digits(digits) |
The value that a SpinButton is currently displaying can be changed using the following method:
spin_button.set_value(value) |
The current value of a SpinButton can be retrieved as either a floating point or integer value with the following methods:
float_value = spin_button.get_value() int_value = spin_button.get_value_as_int() |
If you want to alter the value of a SpinButton relative to its current value, then the following method can be used:
spin_button.spin(direction, increment) |
The direction parameter can take one of the following values:
SPIN_STEP_FORWARD SPIN_STEP_BACKWARD SPIN_PAGE_FORWARD SPIN_PAGE_BACKWARD SPIN_HOME SPIN_END SPIN_USER_DEFINED |
This method packs in quite a bit of functionality, which I will attempt to clearly explain. Many of these settings use values from the Adjustment object that is associated with a SpinButton.
SPIN_STEP_FORWARD and SPIN_STEP_BACKWARD change the value of the SpinButton by the amount specified by increment, unless increment is equal to 0, in which case the value is changed by the value of step_increment in the Adjustment.
SPIN_PAGE_FORWARD and SPIN_PAGE_BACKWARD simply alter the value of the SpinButton by increment.
SPIN_HOME sets the value of the SpinButton to the bottom of the Adjustment range.
SPIN_END sets the value of the SpinButton to the top of the Adjustment range.
SPIN_USER_DEFINED simply alters the value of the SpinButton by the specified amount.
We move away from methods for setting and retrieving the range attributes of the SpinButton now, and move onto methods that effect the appearance and behavior of the SpinButton widget itself.
The first of these methods is used to constrain the text box of the SpinButton such that it may only contain a numeric value. This prevents a user from typing anything other than numeric values into the text box of a SpinButton:
spin_button.set_numeric(numeric) |
numeric is TRUE to constrain the text entry to numeric values or FALSE to unconstrain the text entry.
You can set whether a SpinButton will wrap around between the upper and lower range values with the following method:
spin_button.set_wrap(wrap) |
The SpinButton will wrap when wrap is set to TRUE.
You can set a SpinButton to round the value to the nearest step_increment, which is set within the Adjustment object used with the SpinButton. This is accomplished with the following method when snap_to_ticks is TRUE:
spin_button.set_snap_to_ticks(snap_to_ticks) |
The update policy of a SpinButton can be changed with the following method:
spin_button.set_update_policy(policy) |
The possible values of policy are:
UPDATE_ALWAYS UPDATE_IF_VALID |
These policies affect the behavior of a SpinButton when parsing inserted text and syncing its value with the values of the Adjustment.
In the case of UPDATE_IF_VALID the SpinButton value only gets changed if the text input is a numeric value that is within the range specified by the Adjustment. Otherwise the text is reset to the current value.
In case of UPDATE_ALWAYS we ignore errors while converting text into a numeric value.
Finally, you can explicitly request that a SpinButton update itself:
spin_button.update() |
The spinbutton.py example program illustrates the use of spinbuttons including setting a number of characteristics. Figure 9.11, “Spin Button Example” shows the result of running the example program:
The spinbutton.py source code is:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2
3 # example spinbutton.py
4
5 import pygtk
6 pygtk.require('2.0')
7 import gtk
8
9 class SpinButtonExample:
10 def toggle_snap(self, widget, spin):
11 spin.set_snap_to_ticks(widget.get_active())
12
13 def toggle_numeric(self, widget, spin):
14 spin.set_numeric(widget.get_active())
15
16 def change_digits(self, widget, spin, spin1):
17 spin1.set_digits(spin.get_value_as_int())
18
19 def get_value(self, widget, data, spin, spin2, label):
20 if data == 1:
21 buf = "%d" % spin.get_value_as_int()
22 else:
23 buf = "%0.*f" % (spin2.get_value_as_int(),
24 spin.get_value())
25 label.set_text(buf)
26
27 def __init__(self):
28 window = gtk.Window(gtk.WINDOW_TOPLEVEL)
29 window.connect("destroy", lambda w: gtk.main_quit())
30 window.set_title("Spin Button")
31
32 main_vbox = gtk.VBox(False, 5)
33 main_vbox.set_border_width(10)
34 window.add(main_vbox)
35
36 frame = gtk.Frame("Not accelerated")
37 main_vbox.pack_start(frame, True, True, 0)
38
39 vbox = gtk.VBox(False, 0)
40 vbox.set_border_width(5)
41 frame.add(vbox)
42
43 # Day, month, year spinners
44 hbox = gtk.HBox(False, 0)
45 vbox.pack_start(hbox, True, True, 5)
46
47 vbox2 = gtk.VBox(False, 0)
48 hbox.pack_start(vbox2, True, True, 5)
49
50 label = gtk.Label("Day :")
51 label.set_alignment(0, 0.5)
52 vbox2.pack_start(label, False, True, 0)
53
54 adj = gtk.Adjustment(1.0, 1.0, 31.0, 1.0, 5.0, 0.0)
55 spinner = gtk.SpinButton(adj, 0, 0)
56 spinner.set_wrap(True)
57 vbox2.pack_start(spinner, False, True, 0)
58
59 vbox2 = gtk.VBox(False, 0)
60 hbox.pack_start(vbox2, True, True, 5)
61
62 label = gtk.Label("Month :")
63 label.set_alignment(0, 0.5)
64 vbox2.pack_start(label, False, True, 0)
65
66 adj = gtk.Adjustment(1.0, 1.0, 12.0, 1.0, 5.0, 0.0)
67 spinner = gtk.SpinButton(adj, 0, 0)
68 spinner.set_wrap(True)
69 vbox2.pack_start(spinner, False, True, 0)
70
71 vbox2 = gtk.VBox(False, 0)
72 hbox.pack_start(vbox2, True, True, 5)
73
74 label = gtk.Label("Year :")
75 label.set_alignment(0, 0.5)
76 vbox2.pack_start(label, False, True, 0)
77
78 adj = gtk.Adjustment(1998.0, 0.0, 2100.0, 1.0, 100.0, 0.0)
79 spinner = gtk.SpinButton(adj, 0, 0)
80 spinner.set_wrap(False)
81 spinner.set_size_request(55, -1)
82 vbox2.pack_start(spinner, False, True, 0)
83
84 frame = gtk.Frame("Accelerated")
85 main_vbox.pack_start(frame, True, True, 0)
86
87 vbox = gtk.VBox(False, 0)
88 vbox.set_border_width(5)
89 frame.add(vbox)
90
91 hbox = gtk.HBox(False, 0)
92 vbox.pack_start(hbox, False, True, 5)
93
94 vbox2 = gtk.VBox(False, 0)
95 hbox.pack_start(vbox2, True, True, 5)
96
97 label = gtk.Label("Value :")
98 label.set_alignment(0, 0.5)
99 vbox2.pack_start(label, False, True, 0)
100
101 adj = gtk.Adjustment(0.0, -10000.0, 10000.0, 0.5, 100.0, 0.0)
102 spinner1 = gtk.SpinButton(adj, 1.0, 2)
103 spinner1.set_wrap(True)
104 spinner1.set_size_request(100, -1)
105 vbox2.pack_start(spinner1, False, True, 0)
106
107 vbox2 = gtk.VBox(False, 0)
108 hbox.pack_start(vbox2, True, True, 5)
109
110 label = gtk.Label("Digits :")
111 label.set_alignment(0, 0.5)
112 vbox2.pack_start(label, False, True, 0)
113
114 adj = gtk.Adjustment(2, 1, 5, 1, 1, 0)
115 spinner2 = gtk.SpinButton(adj, 0.0, 0)
116 spinner2.set_wrap(True)
117 adj.connect("value_changed", self.change_digits, spinner2, spinner1)
118 vbox2.pack_start(spinner2, False, True, 0)
119
120 hbox = gtk.HBox(False, 0)
121 vbox.pack_start(hbox, False, True, 5)
122
123 button = gtk.CheckButton("Snap to 0.5-ticks")
124 button.connect("clicked", self.toggle_snap, spinner1)
125 vbox.pack_start(button, True, True, 0)
126 button.set_active(True)
127
128 button = gtk.CheckButton("Numeric only input mode")
129 button.connect("clicked", self.toggle_numeric, spinner1)
130 vbox.pack_start(button, True, True, 0)
131 button.set_active(True)
132
133 val_label = gtk.Label("")
134
135 hbox = gtk.HBox(False, 0)
136 vbox.pack_start(hbox, False, True, 5)
137 button = gtk.Button("Value as Int")
138 button.connect("clicked", self.get_value, 1, spinner1, spinner2,
139 val_label)
140 hbox.pack_start(button, True, True, 5)
141
142 button = gtk.Button("Value as Float")
143 button.connect("clicked", self.get_value, 2, spinner1, spinner2,
144 val_label)
145 hbox.pack_start(button, True, True, 5)
146
147 vbox.pack_start(val_label, True, True, 0)
148 val_label.set_text("0")
149
150 hbox = gtk.HBox(False, 0)
151 main_vbox.pack_start(hbox, False, True, 0)
152
153 button = gtk.Button("Close")
154 button.connect("clicked", lambda w: gtk.main_quit())
155 hbox.pack_start(button, True, True, 5)
156 window.show_all()
157
158 def main():
159 gtk.main()
160 return 0
161
162 if __name__ == "__main__":
163 SpinButtonExample()
164 main()
|