The Layout container is similar to the Fixed container except that it implements an infinite (where infinity is less than 2^32) scrolling area. The X window system has a limitation where windows can be at most 32767 pixels wide or tall. The Layout container gets around this limitation by doing some exotic stuff using window and bit gravities, so that you can have smooth scrolling even when you have many child widgets in your scrolling area.
A Layout container is created using:
layout = gtk.Layout(hadjustment=None, vadjustment=None) |
As you can see, you can optionally specify the Adjustment objects (see Chapter 7, Adjustments) that the Layout widget will use for its scrolling. If you don't specify the Adjustment objects, new ones will be created.
You can add and move widgets in the Layout container using the following two methods:
layout.put(child_widget, x, y) layout.move(child_widget, x, y) |
The size of the Layout container can be set and retrieved using the next methods:
layout.set_size(width, height) size = layout.get_size() |
The final four methods for use with Layout widgets are for manipulating the horizontal and vertical adjustment widgets:
hadj = layout.get_hadjustment() vadj = layout.get_vadjustment() layout.set_hadjustment(adjustment) layout.set_vadjustment(adjustment) |
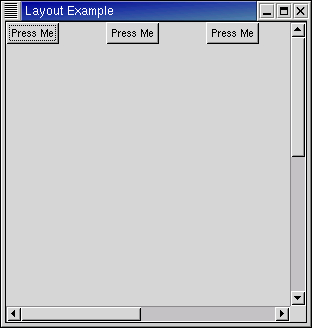
The layout.py example program creates three buttons and puts them in a layout widget. when a button is clicked, it is moved to a random location in the layout. Figure 10.3, “Layout Example” illustrates the starting display of the program:
The layout.py source code is:
1 #!/usr/bin/env python
2
3 # example layout.py
4
5 import pygtk
6 pygtk.require('2.0')
7 import gtk
8 import random
9
10 class LayoutExample:
11 def WindowDeleteEvent(self, widget, event):
12 # return false so that window will be destroyed
13 return False
14
15 def WindowDestroy(self, widget, *data):
16 # exit main loop
17 gtk.main_quit()
18
19 def ButtonClicked(self, button):
20 # move the button
21 self.layout.move(button, random.randint(0,500),
22 random.randint(0,500))
23
24 def __init__(self):
25 # create the top level window
26 window = gtk.Window(gtk.WINDOW_TOPLEVEL)
27 window.set_title("Layout Example")
28 window.set_default_size(300, 300)
29 window.connect("delete-event", self.WindowDeleteEvent)
30 window.connect("destroy", self.WindowDestroy)
31 # create the table and pack into the window
32 table = gtk.Table(2, 2, False)
33 window.add(table)
34 # create the layout widget and pack into the table
35 self.layout = gtk.Layout(None, None)
36 self.layout.set_size(600, 600)
37 table.attach(self.layout, 0, 1, 0, 1, gtk.FILL|gtk.EXPAND,
38 gtk.FILL|gtk.EXPAND, 0, 0)
39 # create the scrollbars and pack into the table
40 vScrollbar = gtk.VScrollbar(None)
41 table.attach(vScrollbar, 1, 2, 0, 1, gtk.FILL|gtk.SHRINK,
42 gtk.FILL|gtk.SHRINK, 0, 0)
43 hScrollbar = gtk.HScrollbar(None)
44 table.attach(hScrollbar, 0, 1, 1, 2, gtk.FILL|gtk.SHRINK,
45 gtk.FILL|gtk.SHRINK, 0, 0)
46 # tell the scrollbars to use the layout widget's adjustments
47 vAdjust = self.layout.get_vadjustment()
48 vScrollbar.set_adjustment(vAdjust)
49 hAdjust = self.layout.get_hadjustment()
50 hScrollbar.set_adjustment(hAdjust)
51 # create 3 buttons and put them into the layout widget
52 button = gtk.Button("Press Me")
53 button.connect("clicked", self.ButtonClicked)
54 self.layout.put(button, 0, 0)
55 button = gtk.Button("Press Me")
56 button.connect("clicked", self.ButtonClicked)
57 self.layout.put(button, 100, 0)
58 button = gtk.Button("Press Me")
59 button.connect("clicked", self.ButtonClicked)
60 self.layout.put(button, 200, 0)
61 # show all the widgets
62 window.show_all()
63
64 def main():
65 # enter the main loop
66 gtk.main()
67 return 0
68
69 if __name__ == "__main__":
70 LayoutExample()
71 main()
|